1. 前言
babel是逆向js的一大利器,对于不了解使用babel逆向javascript的我推荐看以下这篇文章:逆向进阶,利用 AST 技术还原 JavaScript 混淆代码
其中也有一些很有用的网站:AST explorer :可以在线解析AST树,在分析代码的过程中很有帮助,使用时记得在网站顶部把编译器换成@babel/parser。@babel/types文档 :查babel的node名称和属性基本上就靠他了。Babel 插件手册 :介绍了如何使用babel进行AST转换。
但是在实际使用中,由于babel的特性/bug比较多,逆向过程中会有很多问题,所以才有了这么一篇踩坑文章。
2. babel特性
由于在AST转换过程中直接给node赋值无法自动修改node中包含的引用,所以要在path上使用replaceWith函数进行替换node,但是这个replaceWith函数本身就有很多特性,所以会在使用的时候有很多意料之外的情况,具体来说他会:
在replaceWtih后不会删去原来node包含的引用(references、referenced和referencePaths)
replaceWith增加的新节点不一定会添加引用(没有仔细测试,貌似如果一个node经过两次clone他就无法在replaceWith时增加引用?)同样replaceWith也不会更新constantViolations
同时traverse也会有一些神奇的特性,比如在使用path.traverse的时候,不会遍历到path节点,这就会导致有时候traverse结果和想象中的不一样。
总之我们在使用babel进行逆向去混淆的过程中一定要仔细处理node中包含的引用,否则ast中错误的reference会对后续的去混淆造成影响,无论是存在无效的reference(导致节点始终在被引用的状态,且遍历reference时node可能无效)还是缺少reference(在根据reference处理node时可能会造成某些node遗漏未被处理)。
2.1. 解决方案
对于这种replaceWith无法很好的更新引用的情况,我们可以在replaceWith前后手动修复引用,但是对于constantViolations,我实在是不想处理了:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 function fixReference (path ) { function _fixReference (identifierPath ) { const binding = path.scope .getBinding (identifierPath.node .name ); if (binding === undefined ) return ; if (binding.referencePaths .indexOf (identifierPath) !== -1 ) return ; binding.referencePaths .push (identifierPath); binding.references = binding.referencePaths .length ; binding.referenced = binding.references !== 0 ; } if (path.node .type === "Identifier" ) { _fixReference (path); } else { path.traverse ({ Identifier (identifierPath) { _fixReference (identifierPath); } }) } } function removeReference (path ) { function _removeReference (identifierPath ) { const binding = path.scope .getBinding (identifierPath.node .name ); if (binding === undefined ) return ; const idx = binding.referencePaths .indexOf (identifierPath); if (idx > -1 ) { binding.referencePaths .splice (idx, 1 ); binding.references = binding.referencePaths .length ; binding.referenced = binding.references !== 0 ; } } if (path.node .type === "Identifier" ) { _removeReference (path); } else { path.traverse ({ Identifier (identifierPath) { _removeReference (identifierPath); } }) } } function replaceWith (path, node ) { removeReference (path); path.replaceWith (node); fixReference (path); }
3. JavaScript逆向
3.1. 字符串编码
我们先来考虑一些简单的场景:字符串编码混淆
1 2 3 4 5 6 console .log ("Hello World!" );console .log ("'\" \\" );console .log ('Hello\x20World!' );console .log ('\x27\x22\x20\x5c' );
AST树 :
在逆向的过程中可以使用以下Visitor反混淆:
1 2 3 4 5 const stringDecodeVisitor = { StringLiteral (path) { delete path.node .extra } }
由于根据babel文档,StringLiteral 只有value属性是必须的有的,所以直接删掉extra属性就行了。
3.2. 无用变量
在反混淆的过程中随着代码简化,会有很多变量不再被引用,此时我们可以通过如下Vistor去除:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 const removeSymbolVisitor = { VariableDeclarator (path) { const binding = path.scope .getBinding (path.node .id .name ); if (!binding || binding.constantViolations .length > 0 ) { return ; } if (!binding.referenced ) { path.remove (); } } }
其中constantViolations可能不太好理解,举个例子,以下两行代码(即a的赋值和a的自增)均会增加a的constantViolations:
目前来看还有留着这种变量的需要,因为有的时候变量值不重要但是赋值操作很重要,比如如下情况:
这种情况下虽然a没有reference但是删掉a会导致eval(b)消失,从而导致代码逻辑错误。
3.3. const变量
1 2 3 4 5 console .log (1 , 1 );const a=1 ,b=a;console .log (a,b);
其中只要找到type为const的VariableDeclaration 并在其中找init类型为Literal或Identifier的常量,替换其中的引用即可。
Visitor如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 const inlineConstValueVisitor = { VariableDeclaration (path) { if (path.node .kind !== "const" ) return ; path.get ("declarations" ).forEach (function (path ) { if (path.node .init === null ) return ; if (!(types.isLiteral (path.node .init ) || path.node .init .type === "Identifier" )) return ; path.scope .getBinding (path.node .id .name ).referencePaths .slice ().forEach (function (_path ) { replaceWith (_path, types.cloneDeepWithoutLoc (path.node .init )); }); removeReference (path); path.remove (); }); } }
3.4. 多余逻辑判断
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 console .log (1 );console .log (4 );if (true ){ console .log (1 ); } if (false ){ console .log (2 ); } if (false ){ console .log (3 ); }else { console .log (4 ); } while (false ){ console .log (5 ); }
其中IfStatement 包含test、consequent、alternate三个node,alternate可以为null,我们可以根据test计算结果来替换分支逻辑。
而WhileStatement 包含test和body,只有在test结果为false时才可以把整个While删去。
Visitor如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 const unreachablePathVisitor = { "IfStatement|ConditionalExpression" (path) { const { confident, value } = path.get ("test" ).evaluate(); if (confident) { if (value) { replaceWith (path, types.cloneDeepWithoutLoc (path.node .consequent )); } else { if (path.node .alternate !== null ) { replaceWith (path, types.cloneDeepWithoutLoc (path.node .alternate )); } else { removeReference (path); path.remove (); } } } }, WhileStatement (path) { const { confident, value } = path.get ("test" ).evaluate(); if (confident && value === false ) { removeReference (path); path.remove (); } } }
3.5. 多余的BlockStatement块
有时候我们在替换node后有些BlockStatement块就显得多余了,比如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 if (true ){ console .log ('Hello World!' ); } { console .log ('Hello World!' ); }
此时AST 如图:
此时我们可以判断replaceWith的node是否为BlockStatement,如果是他的body数组长度是否为1,如果为1我们可以直接用他的body[0]去替换这个BlockStatement。
我们将上文的replaceWith改成如下形式即可达到replace的过程中自动化简BlockStatement的目的:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 function replaceWith (path, node ) { function tryUnwarpBlockStatement (node ) { if (node.type !== "BlockStatement" || node.body .length !== 1 ) return node; else return node.body [0 ]; } removeReference (path); path.replaceWith (tryUnwarpBlockStatement (node)); fixReference (path); }
3.6. 表达式混淆
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 const a = "string" ;const b = false ;const b = false ;const b = true ;const a = "str" +"ing" ;const b = "123" =="456" ;const c = ![];const d = !![];
对此我们可以尝试对表达式求值,如果evaluate结果为confident我们就可以用value做替换:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 const evalVisiotr = { "UnaryExpression|BinaryExpression|CallExpression|ConditionalExpression" (path) { const { confident, value } = path.evaluate(); if (confident) { removeReference (path); path.replaceInline (types.valueToNode (value)); path.skip (); } } }
3.7. 以数组下标方式访问成员函数
1 2 3 4 //混淆前 console.log('Hello World!'); //混淆后 console['log']('Hello World!');
AST树 :
其中访问成员函数的node为MemberExpression ,其中computed变量代表是否以数组下标方式访问,property为访问的函数名称,这里将computed设置为false并将property设置为字符串的值来还原成员函数的访问。
反混淆用的Visitor代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 const callFunctionReverseVisitor = { CallExpression (path) { if (path.node .callee .type === "MemberExpression" ) { const callee = path.node .callee ; if (callee.computed === true && callee.property .type === "StringLiteral" ) { callee.computed = false const idxPath = path.get ("callee.property" ) replaceWith (idxPath,types.identifier (callee.property .value )) } } } }
3.8. 替换执行函数
此时func里面可能包含一些反反混淆代码,可能是debuger检测,也可能是代码格式化检查等。如果我们希望自己定义func并执行计算结果就可以用如下Visitor
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 function functionEvalVisitor (funcName, func ) { return { CallExpression (path) { if (path.node .callee .type === "Identifier" && path.node .callee .name === funcName) { removeReference (path); const evaluate = path.get ("arguments" ).map ((path ) => { return path.evaluate() }); if (evaluate.every ((eval { return eval .confident })) { const args = evaluate.map ((eval { return eval .value }); const value = func (...args); switch (typeof value) { case "string" : path.replaceInline (types.stringLiteral (value)); break ; case "number" : path.replaceInline (types.numericLiteral (value)); break ; case "boolean" : path.replaceInline (types.booleanLiteral (value)); break ; case "undefined" : path.replaceInline (types.identifier ('undefined' )); break ; default : throw new Error ("Unsupported return type" ); } } } } } }
3.9. 控制流平坦化
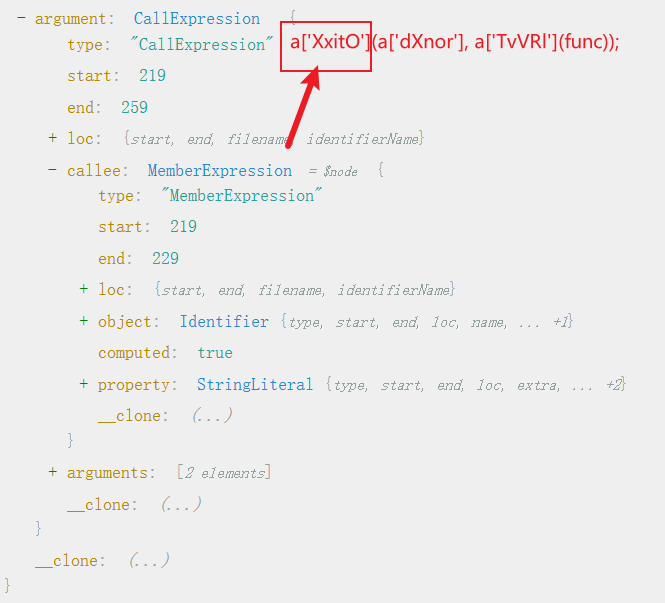
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 function getStr ( return "aaaaaaaa" +func (); } function getStr ( var a = { 'XxitO' : function (b, c ) { return b + c; }, 'dXnor' : 'aaaaaaaa' , 'TvVRl' : function (b ) { return b (); } }; return a['XxitO' ](a['dXnor' ], a['TvVRl' ](func)); }
AST树 :
我们可以根据MemberExpression去找他引用的对象,然后去对象的init.properties找字典对应的值,然后把这个值给替换过来:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 const removeMemberExpressionVisitor = { MemberExpression (path) { if (path.node .property .type == 'StringLiteral' ) { const binding = path.scope .getBinding (path.node .object .name ) if (binding !== undefined ) { const objPath = binding.path if (objPath.node .init !== undefined && objPath.node .init .type === 'ObjectExpression' ) { const objPropertiesPath = objPath.get ("init.properties" ) const propertyPath = objPropertiesPath.find ((_path ) => { return _path.node .type === 'ObjectProperty' && _path.node .key .type === 'StringLiteral' && _path.node .key .value === path.node .property .value }) if (propertyPath === undefined ) return ; const node = propertyPath.node ; const value = node.value ; if (types.isLiteral (value)) { replaceWith (path, types.cloneDeepWithoutLoc (node.value )) } else if (value.type === 'FunctionExpression' ) { if (value.id === null && value.generator === false && value.async === false && hasSingleStatement (value) && isRecursionFunction (propertyPath.get ('value' )) === false ) { replaceWith (path, types.cloneDeepWithoutLoc (node.value )); } } else { return ; } } } } } }
运行后效果如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 function getStr ( var a = { "XxitO" : function (b, c ) { return b + c; }, "dXnor" : "aaaaaaaa" , "TvVRl" : function (b ) { return b (); } }; return function (b, c ) { return b + c; }("aaaaaaaa" , function (b ) { return b (); }(func)); }
首先不得不承认它更丑了,但你就说控制流平坦化解没解决吧(大雾),上面的var a可以用removeSymbolVisitor去除,而下面的FunctionExpression我们后续再处理。
3.10. 函数调用混淆
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 func (0x400 - 233 , 0x200 );func (123 , 456 );console .log (1 - 2 - 3 , [4 , 5 , 6 , 7 ]);console .log (1 - 2 - 999 , []);console .log (3 - 4 - 3 , []);function a (a, b, c, d, e, f ) { return func (d - 233 , b); } a (0x100 , 0x200 , 0x300 , 0x400 , 0x500 , 0x600 );(function (a, b ) { return func (a, b); })(123 , 456 ); function b (a, b, c = 3 , ...d ) { return console .log (a - b - c, d); } b (1 , 2 , undefined , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 );b (1 , 2 , 999 );b (3 , 4 );
这两种情况我们分开考虑,对于FunctionDeclaration我们只要将函数a给内联即可,随后他会变成第二种FunctionExpression的状态,首先我们要确定我们可以inline的代码,对于复杂的函数我们不动:
1 2 3 function hasSingleStatement (funcNode ) { return funcNode.body .type === 'BlockStatement' && funcNode.body .body .length === 1 && funcNode.body .body [0 ].type === "ReturnStatement" ; }
这个代码会判断一个函数是否只有一个return代码块,只有满足条件才会返回true。
其次这个函数还不能递归,递归内联的话就寄了:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 function isRecursionFunction (funcPath ) { if (funcPath.node .id === null ) return false ; let ret = false ; funcPath.traverse ({ enter (path ) { if (funcPath.parentPath .scope .bindings [funcPath.node .id .name ].referencePaths .some (function (refPath ) { return refPath.node === path.node ; })) { ret = true ; path.stop (); } } }) return ret; }
然后我们遍历FunctionDeclaration,将所有满足调教的函数从FunctionDeclaration内联成FunctionExpression,这个过程要仔细处理变量引用,相当的麻烦:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 function inlineNamedFunction (path ) { const node = path.node if (!hasSingleStatement (node)) return ; if (node.generator || node.async ) return ; if (isRecursionFunction (path)) return ; if (node.id !== null ) { const name = node.id .name ; const binding = path.scope .parent .bindings [name]; _referencePaths = [] binding.referencePaths .slice ().forEach (function (nodePath ) { if (nodePath.parent .type === "CallExpression" ) { _node = types.cloneDeepWithoutLoc (node); nodePath.replaceWith (types.functionExpression (null , _node.params , _node.body , _node.generator , _node.async )); inlineFunction (nodePath, nodePath.parentPath ); } else { _referencePaths.push (nodePath); } }); binding.referencePaths = _referencePaths; binding.references = _referencePaths.length ; binding.referenced = binding.references !== 0 ; } } const inlineFunctionDeclarationVisitor = { FunctionDeclaration (path) { if (path.node .id ) inlineNamedFunction (path); if (!(path.node .id && path.scope .parent .bindings [path.node .id .name ].referenced )) { removeReference (path); path.remove (); } } }
这时候我们再来处理FunctionExpression,我们遍历所有CallExpression,检查调用的目标是否为FunctionExpression,这个FunctionExpression也有id属性,因此FunctionDeclaration该做的检查他是一点都不能少啊:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 const inlineFunctionExpressionVisitor = { CallExpression (path) { if (path.node .callee .type === 'FunctionExpression' && hasSingleStatement (path.node .callee )) { if (path.node .callee .id !== null ) inlineNamedFunction (path.get ("callee" )); inlineFunction (path.get ("callee" ), path); } } }
然后我们实现具体的内联功能,其中functionExpression的params真的是多种多样,而引用一处理不好也会寄,总之直接看代码吧:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 function inlineFunction (func, call ) { const arg = call.node .arguments ; func.node .params .forEach (function (param, idx ) { let paramName; if (types.isIdentifier (param)) { paramName = param.name ; } else if (types.isPattern (param)) { if (param.left .type !== "Identifier" ) throw new Error ('unknown node type' ); paramName = param.left .name ; } else if (types.isRestElement (param)) { if (param.argument .type !== "Identifier" ) throw new Error ('unknown node type' ); paramName = param.argument .name ; } func.scope .bindings [paramName].referencePaths .slice ().forEach (function (path ) { if (path.node .type === "Identifier" ) { if (types.isIdentifier (param)) { removeReference (path); path.replaceWith ((arg[idx] === undefined ? types.identifier ("undefined" ) : types.cloneDeepWithoutLoc (arg[idx]))); } else if (types.isPattern (param)) { removeReference (path); path.replaceWith (types.cloneDeepWithoutLoc ((arg[idx] === undefined || arg[idx].value === undefined ) ? param.right : arg[idx])); } else if (types.isRestElement (param)) { removeReference (path); path.replaceWith (types.arrayExpression (arg.slice (idx))); } } else { throw new Error ('unknown node type' ); } }) }) replaceWith (call, types.cloneDeepWithoutLoc (func.node .body .body [0 ].argument )); }
3.11. 使用switch的控制流平坦化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 console .log ("0" );console .log ("1" );console .log ("2" );console .log ("3" );console .log ("4" );console .log ("5" );var aaaaaa = ["2" , "0" , "3" , "4" , "1" , "5" ];var bbbbbb = 0x0 ;while (true ) { switch (aaaaaa[bbbbbb++]) { case "0" : console .log ("1" ); continue ; case "1" : console .log ("4" ); continue ; case "2" : console .log ("0" ); continue ; case "3" : console .log ("2" ); continue ; case "4" : console .log ("3" ); continue ; case "5" : console .log ("5" ); continue ; } break ; }
这里我们找到控制执行流程的数组,然后按照数组顺序还原代码即可:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 const switchControlsFlowFlatteningVisitor = { WhileStatement (path) { const { confident : whileConfident, value : whileValue } = path.get ("test" ).evaluate(); if (!(whileConfident === true && whileValue === true )) return ; if (!(path.node .body .type === "BlockStatement" )) return ; const whileBodyNode = path.node .body ; if (!(whileBodyNode.body .length === 2 && whileBodyNode.body [0 ].type === "SwitchStatement" && whileBodyNode.body [1 ].type === "BreakStatement" )) return ; const switchBodyNode = whileBodyNode.body [0 ]; if (!(switchBodyNode.discriminant .type === "MemberExpression" && switchBodyNode.discriminant .object .type === "Identifier" )) return ; const listBinding = path.scope .getBinding (switchBodyNode.discriminant .object .name ) if (listBinding === undefined ) return ; if (!(listBinding.path .node .type === "VariableDeclarator" && listBinding.path .node .init !== null )) return ; const { confident : listConfident, value : listValue } = listBinding.path .get ("init" ).evaluate(); if (!(listConfident === true && Array .isArray (listValue))) return ; const consequent = Object .fromEntries (switchBodyNode.cases .map (x =>test .value , x.consequent ])); newCode = listValue.map (x => if (newCode.some ((x ) => x === undefined )) return ; if (newCode.some ((x ) => x.at (-1 ).type !== "ContinueStatement" )) return ; newCode = newCode.map ((x ) => x.slice (0 , -1 )); newCode = newCode.flat (); newCode = newCode.map ((x ) => types.cloneDeepWithoutLoc (x)); newCodeStatement = types.blockStatement (newCode); replaceWith (path, newCodeStatement); } }
4. 后记
文章里出现的visitor可以在visitor.js 中找到,代码未经过严格测试,可能包含一些bug(至少已知不会处理path的constantViolations值,并且在内联函数的过程中不会处理通过arguements访问的参数),但是日常使用应该问题不大,总之babel很强大,但是bug少点就好了(悲)。